When we want to make a simple cube using Python in Grasshopper, we can simply use Addbox function in Rhinoscriptsyntax. Just like below.
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
#points should be coordinates in (x,y,z) form
point_list = [p1,p2,p3,p4,p5,p6]
rs.AddBox(point_list)The function takes 8 point lists which consist of the cube that we are going to make. However, important thing is that the point list items should be in the order of the below image to create a normal cube.
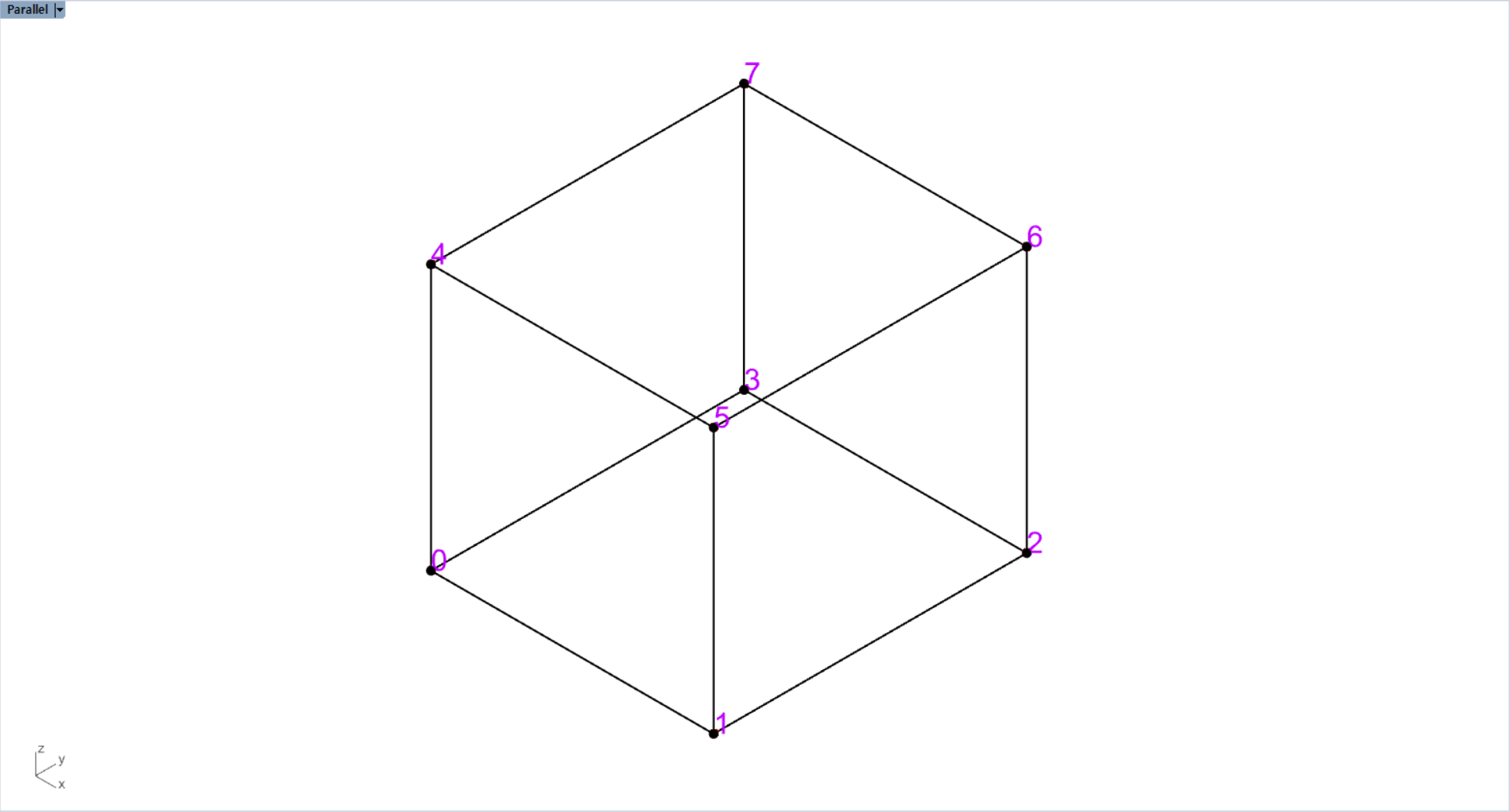
From the below point, the points rotate in reversed clockwise.
Then how can we manage those vertices to be in order? At this point, we need some basic knowledge regarding Python, dealing with sorting lists. The first thing we are going to use is the function sorted() and the second one is the item swap.
(1) sorted ( )
list = [1,55,2,8,20,19,23,27,3]
print list
sorted_list = sorted(list)
print sorted_list[1, 55, 2, 8, 20, 19, 23, 27, 3]
[1, 2, 3, 8, 19, 20, 23, 27, 55]As you can see on the upper code, the sorted() function automatically returns the list sorted in ascending order. However, sorting points is a bit more complex question. The reason is that there are x,y,z coordinates in our list items. (It is not constructed with a single number like upper example) Then in this situation, what will be our strategy?
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
vertice_list = [(0,0,0),(40,0,0),(40,0,40),(0,0,40),(40,40,0),(40,40,40),(0,40,0),(0,40,40)]
a = rs.AddBox(vertice_list)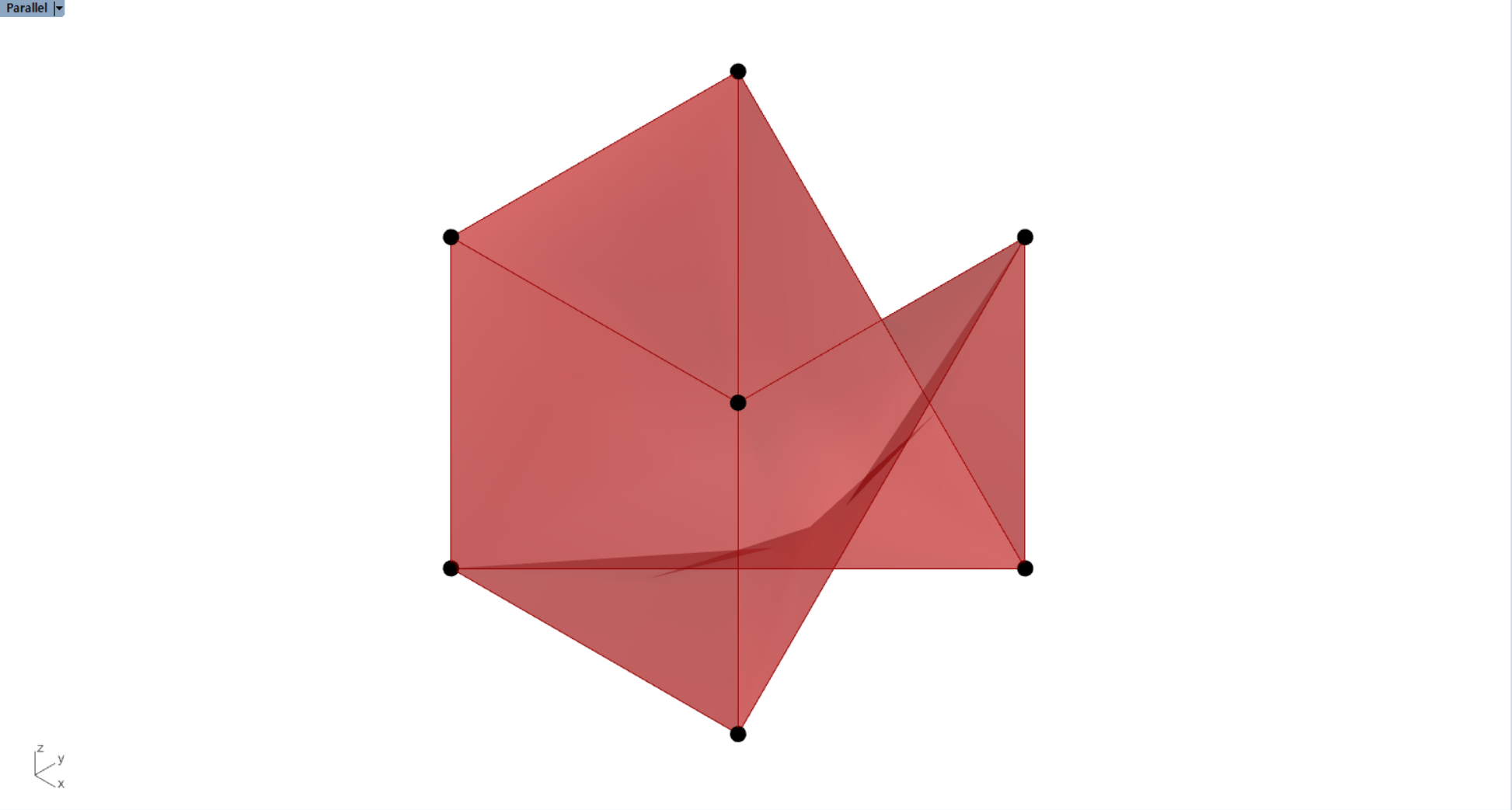
Using options of sorted() function, we can firstly sort points similar to our intention.
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
vertice_list = [(0,0,0),(40,0,0),(40,0,40),(0,0,40),(40,40,0),(40,40,40),(0,40,0),(0,40,40)]
vertice_list = sorted(vertice_list, key=lambda x : x[2])
print vertice_list
a = rs.AddBox(vertice_list)[(0, 0, 0), (40, 0, 0), (40, 40, 0), (0, 40, 0), (40, 0, 40), (0, 0, 40), (40, 40, 40), (0, 40, 40)]Using the key option in the sorted function, we can sort a list by the reference we allocated. In the upper example, the list was sorted by z coordinates. However, we still need to sort points, especially orders of vertice_list[4] and vertice_list[5] are switched. In this case, we can use item swap function.
(2) item swap
Item swap is a simple and powerful tool when we have to manipulate the order of two items. The syntax is as below.
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
vertice_list = [(0,0,0),(40,0,0),(40,0,40),(0,0,40),(40,40,0),(40,40,40),(0,40,0),(0,40,40)]
vertice_list = sorted(vertice_list, key=lambda x : x[2])
print vertice_list
vertice_list[4], vertice_list[5] = vertice_list[5], vertice_list[4]
print vertice_list
a = rs.AddBox(vertice_list)[(0, 0, 0), (40, 0, 0), (40, 40, 0), (0, 40, 0), (0, 0, 40), (40, 0, 40), (40, 40, 40), (0, 40, 40)]Finally, points are sorted as box generating order.
(3) Result
Now, the box will be generated with no errors.
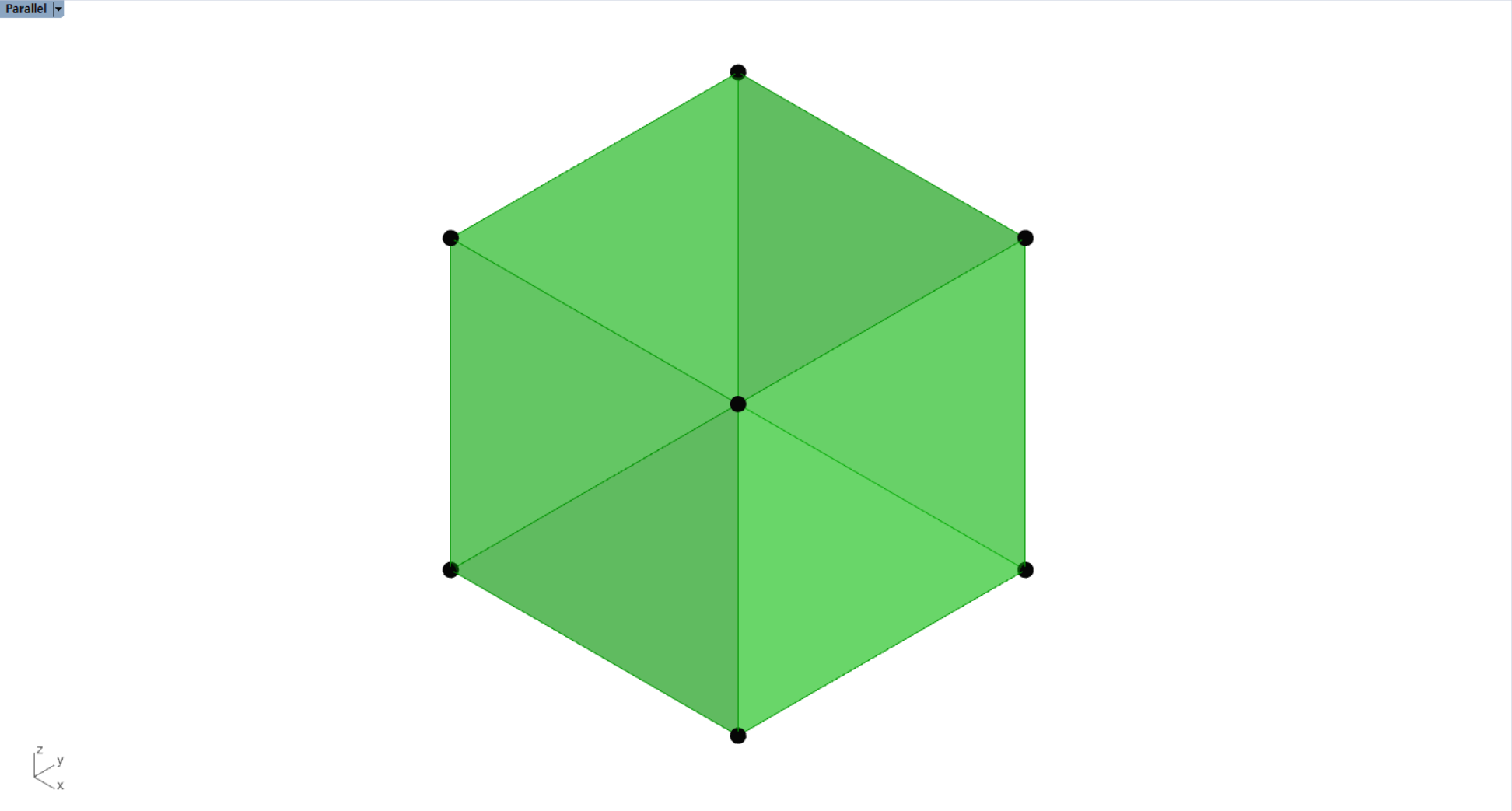
'Python & Coding > Python in Grasshopper' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 그래스호퍼에서 비트맵 이미지 벡터화하기 1 (0) | 2023.06.03 |
|---|---|
| Dealing with tree structures in Python Grasshopper (0) | 2021.06.18 |
| 라이노 그래스호퍼에서 파이썬 사용하기 (0) | 2021.06.03 |